F50 Engine
More than anything else, a Ferrari is an engine. They are famous as V12s, although a
fair number are configured otherwise. Beyond the exotic, almost hedonistic nature of
the V12 and abundance of power as reason for its existance, there is the
sound of multiple explosions and the distinctive chorus that a mechanically complex
engine creates.
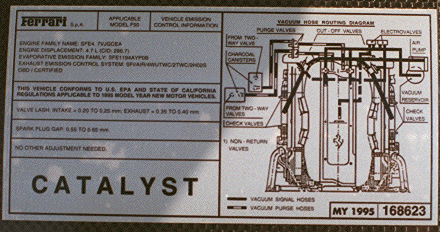
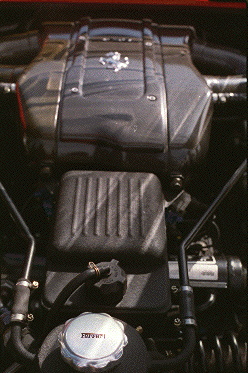
The F50 continues the tradition of the F40, in that the engine
configuration reflects the Formula 1 engine specifications at the time of its manufacture. The F40 featured a turbocharged V8, as Formula 1 rules at the time dictated small engine displacement
coupled with turbocharging. The rules were changed by 1995 to ban turbos but allow larger
engines. Thus the F50 displaces 4.7 liters and is normally aspirated.
The cylinder heads are aluminum and feature five valves per cylinder; three intake and
two exhaust. They are actuated by four overhead chain driven camshafts. The
intake is a variable geometry design. A Bosch engine management system supervises the
fuel injection and ignition tasks. The exhaust escapes via a stainless steel
"six-into-two-into-one" system. An electronically controlled valve switches between two
exhaust system lengths, one for low speed torque, the other for high speed power. The F50
engine meets all US emission requirements, including the tough California laws.

Specifications
| Designation: |
F130 |
| Configuration: |
V12, 65 degrees. |
| Main Bearings: |
Seven |
| Displacement: |
4698 cc. (286.7 cubic inches) |
| Bore and Stroke: |
85 mm. x 69 mm. (3.35" x 2.72") |
| Compression Ratio: |
11.3:1 |
| Power: |
513 bhp @ 8500 rpm; 109 HP/litre (SAE) |
| Torque: |
347 ft.-lb. @ 6500 rpm |
| Redline: |
8500 rpm |
| Oil Capacity: |
12.2 quarts |
| Cooling Capacity: |
18.0 quarts |
| Weight: |
436.5 lb |


|







